Understanding Einstein’s Theory
Einstein’s theories of relativity revolutionized our understanding of the universe. They are deeply connected to the concept of dimensions, particularly space and time. Here’s a breakdown of the theory in both contexts:
Einstein’s Theory Without Time-Space Dimensions
-
Key Idea: Energy-Mass Relationship
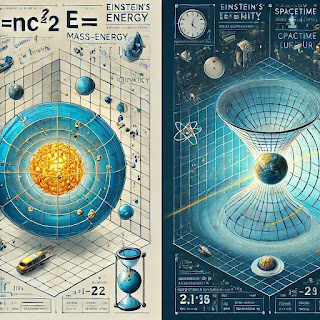
Einstein's famous equation, , shows that energy () and mass () are interchangeable, connected by the speed of light squared ().- This equation explains phenomena like nuclear energy, where small amounts of mass are converted into vast amounts of energy.
-
Implications:
- It does not explicitly involve spatial or temporal dimensions but describes how mass and energy interact universally.
- Foundation for understanding processes like nuclear reactions and star lifecycles.
Einstein’s Theory with Time-Space Dimensions
-
Special Relativity (1905):
- Space and time are not separate entities but a single continuum called spacetime.
- Time dilation: Moving objects experience time slower compared to stationary ones.
- Example: Astronauts traveling near the speed of light age slower than people on Earth.
- Length contraction: Objects in motion contract in the direction of movement as they approach the speed of light.
Key Formula:
Where is the dilated time, is the stationary time, is the velocity, and is the speed of light.
-
General Relativity (1915):
- Gravity is not a force but the warping of spacetime by massive objects.
- Objects follow the curved paths in spacetime, like planets orbiting stars.
- Predicts phenomena like black holes and gravitational waves.
Key Equation: Einstein’s field equations relate spacetime curvature () to energy and matter ():
Illustrative Examples
-
Without Dimensions:
Imagine mass-energy conversion in a nuclear reactor—no explicit reference to time or space is required to understand the transformation. -
With Dimensions:
The bending of light near a massive object (gravitational lensing) demonstrates spacetime warping. GPS systems correct for time dilation caused by Earth’s gravity, showcasing relativity's practical application.
Impact of Einstein’s Theories
- Technology: GPS, nuclear energy, and advanced space exploration.
- Philosophy: A deeper understanding of time and space reshaped human perception of reality.
- Astronomy: Explains the behavior of black holes, expansion of the universe, and cosmic phenomena.
Here is an educational illustration of Einstein's theory of relativity, demonstrating both mass-energy equivalence and spacetime curvature. Let me know if additional elements or adjustments are needed!






0 Comments